https://www.codebyamir.com/blog/java-developers-guide-to-ssl-certificates
Overview
When developing web applications, we often need to integrate with other applications using SSL. This could be over different protocols such as HTTPS, IMAPS, or LDAPS.
In this article, we‘ll cover what Java developers need to know about SSL certificates.
Certificate Chain
An SSL connection succeeds only if the client can trust the server. Let‘s take a look at how this trust model works.
In Chrome, go to google.com and bring up the Developer Tools (F12 on Windows, Cmd+Option+i on Mac).
Under the Security tab, click the View Certificate button to show details about the certificate.
We can see that the site certificate is part of a chain. This particular chain consists of 3 certificates.
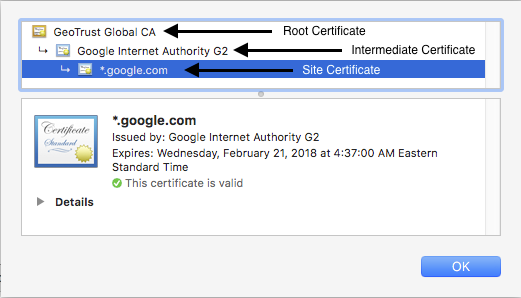
Certificate chain for google.com
The site certificate has been issued by a certificate named Google Internet Authority G2. This is the intermediate certificate. In turn, the intermediate certificate is issued by the root certificate GeoTrust Global CA.
When we establish a connection over HTTPS, the web server will respond by providing its site and intermediate certificates. It is then up to the client to complete the chain by having the root certificate. This chain validation is necessary for the client to trust the site.
Since Chrome has the root certificate GeoTrust Global CA in its certificate store, our connection succeeds and we are not presented with any errors or warnings.
Note: There may be more than one intermediate certificate in the chain depending on the site.
Self-signed Certificates
Certificates not issued by known CA but rather by the server hosting the certificate are called self-signed.
These are often used in internal development environments that are not customer facing.
The root certificates for these will be absent in the browser‘s certificate store.
An example of self-signed certificate is at https://self-signed.badssl.com. We can see that this was issued by Avast Untrusted CA which the browser does not recognize so it displays a warning.
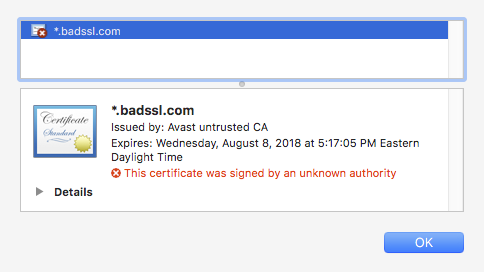
Self-signed certificate
Java Truststore & KeyStore
In this section, we‘ll discuss where certificates live on a system where the JDK/JRE is installed.
Truststore
The truststore is a file that contains the root certificates for Certificate Authorities (CA) that issue certificates such as GoDaddy, Verisign, Network Solutions, and others.
The truststore comes bundled with the JDK/JRE and is located in $JAVA_HOME/lib/security/cacerts.
The truststore is used whenever our Java code establishes a connection over SSL.
Keystore
The keystore is a file used by an application server to store its private key and site certificate.
So if we were running a web application over SSL at tomcat.codebyamir.com, the keystore file named keystore.jks would contain two entries - one for the private key and one for the certificate.
The keystore is used by Java application servers such as Tomcat to serve the certificates.
Note: Most Java application servers only read the contents of these files during startup. This means that any updates to the file require a restart to take effect.
Keytool
Keytool is a utility bundled with the JRE for managing key pairs and certificates. This allows us to view/modify/create certificate stores in the Java world.
List the certificates in the truststore
keytool -list -keystore $JAVA_HOME/lib/security/cacertsWe‘ll be prompted for a password for the truststore. The default password is "changeit".
This truststore contains 104 entries and each entry has a unique alias and fingerprint. We‘ve truncated the output below for brevity.
Keystore type: JKS
Keystore provider: SUN
Your keystore contains 104 entries
verisignclass2g2ca [jdk], Aug 25, 2016, trustedCertEntry,
Certificate fingerprint (SHA1): B3:EA:C4:47:76:C9:C8:1C:EA:F2:9D:95:B6:CC:A0:08:1B:67:EC:9D
digicertassuredidg3 [jdk], Aug 25, 2016, trustedCertEntry,
Certificate fingerprint (SHA1): F5:17:A2:4F:9A:48:C6:C9:F8:A2:00:26:9F:DC:0F:48:2C:AB:30:89
verisignuniversalrootca [jdk], Aug 25, 2016, trustedCertEntry,
Certificate fingerprint (SHA1): 36:79:CA:35:66:87:72:30:4D:30:A5:FB:87:3B:0F:A7:7B:B7:0D:54
digicerttrustedrootg4 [jdk], Aug 25, 2016, trustedCertEntry,
Certificate fingerprint (SHA1): DD:FB:16:CD:49:31:C9:73:A2:03:7D:3F:C8:3A:4D:7D:77:5D:05:E4
verisignclass1g3ca [jdk], Aug 25, 2016, trustedCertEntry,
Certificate fingerprint (SHA1): 20:42:85:DC:F7:EB:76:41:95:57:8E:13:6B:D4:B7:D1:E9:8E:46:A5
identrustpublicca [jdk], Aug 25, 2016, trustedCertEntry,
Certificate fingerprint (SHA1): BA:29:41:60:77:98:3F:F4:F3:EF:F2:31:05:3B:2E:EA:6D:4D:45:FD
utnuserfirstobjectca [jdk], Aug 25, 2016, trustedCertEntry,
Certificate fingerprint (SHA1): E1:2D:FB:4B:41:D7:D9:C3:2B:30:51:4B:AC:1D:81:D8:38:5E:2D:46
geotrustuniversalca [jdk], Aug 25, 2016, trustedCertEntry,
Certificate fingerprint (SHA1): E6:21:F3:35:43:79:05:9A:4B:68:30:9D:8A:2F:74:22:15:87:EC:79
digicertglobalrootg3 [jdk], Aug 25, 2016, trustedCertEntry,
Certificate fingerprint (SHA1): 7E:04:DE:89:6A:3E:66:6D:00:E6:87:D3:3F:FA:D9:3B:E8:3D:34:9E
deutschetelekomrootca2 [jdk], Aug 25, 2016, trustedCertEntry,
Certificate fingerprint (SHA1): 85:A4:08:C0:9C:19:3E:5D:51:58:7D:CD:D6:13:30:FD:8C:DE:37:BF
...Using the google.com example from before, let‘s take a look at the fingerprint for the GeoTrust Global CA from our browser:
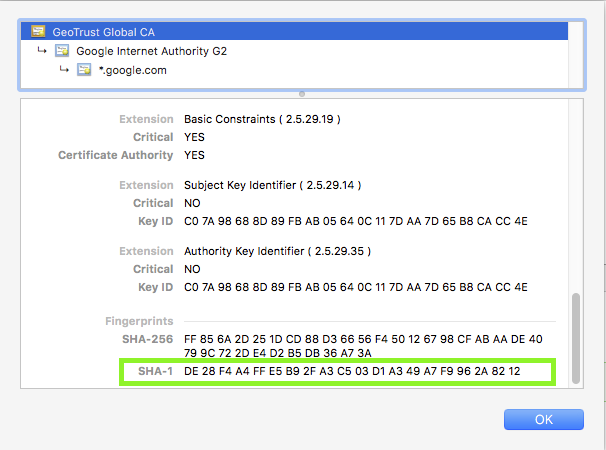
Root CA certificate for google.com
The SHA-1 fingerprint is DE:28:F4:A4:FF:E5:B9:2F:A3:C5:03:D1:A3:49:A7:F9:96:2A:82:12
Let‘s look for that in our truststore:
keytool -list -keystore $JAVA_HOME/lib/security/cacerts | grep -B1 -i DE:28
Enter keystore password: changeit
geotrustglobalca [jdk], Aug 25, 2016, trustedCertEntry,
Certificate fingerprint (SHA1): DE:28:F4:A4:FF:E5:B9:2F:A3:C5:03:D1:A3:49:A7:F9:96:2A:82:12The output tells us that the certificate is in the truststore.
What does this mean to a Java developer?
It means that code connecting to https://www.google.com won‘t throw an exception due to an SSL handshake error.
Add a certificate to the truststore
Adding a certificate to the truststore is necessary if we want to trust a certificate issued from a CA not present in the bundled truststore.
keytool -import -trustcacerts -file [certificate] -alias [alias] -keystore $JAVA_HOME/lib/security/cacertsCode Example
Below is some Java code that will connect to a URL and print the contents of the page onto the screen.
package com.codebyamir.ssl;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLConnection;
public class App {
private static final String URL = "https://www.google.com";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
URLConnection conn = connect(URL);
if (conn != null) {
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream()))) {
String input;
while ((input = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(input);
}
}
}
}
public static URLConnection connect(String url) {
URLConnection conn = null;
try {
conn = new URL(url).openConnection();
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
}Connecting to Site with a Trusted Certificate
Let‘s try our code on another site with a valid SSL certificate.
Code
Replace line 12 from the code with this line:
private static final String URL = "https://httpbin.org/user-agent";Output
We can see that the code output successfully shows that our user-agent string is our Java version.
{
"user-agent": "Java/1.8.0_131"
}Connecting to Site with an Untrusted Certificate
Let‘s try our code on a site with a self-signed certificate.
Code
Replace line 12 from the code with this line:
private static final String URL = "https://self-signed.badssl.com";Output
The code throws an SSLHandshakeException because Java doesn‘t trust it.
Exception in thread "main" javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target
at sun.security.ssl.Alerts.getSSLException(Alerts.java:192)
at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.fatal(SSLSocketImpl.java:1949)
at sun.security.ssl.Handshaker.fatalSE(Handshaker.java:302)
at sun.security.ssl.Handshaker.fatalSE(Handshaker.java:296)
at sun.security.ssl.ClientHandshaker.serverCertificate(ClientHandshaker.java:1514)
at sun.security.ssl.ClientHandshaker.processMessage(ClientHandshaker.java:216)
at sun.security.ssl.Handshaker.processLoop(Handshaker.java:1026)
at sun.security.ssl.Handshaker.process_record(Handshaker.java:961)
at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.readRecord(SSLSocketImpl.java:1062)
at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.performInitialHandshake(SSLSocketImpl.java:1375)
at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.startHandshake(SSLSocketImpl.java:1403)
at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.startHandshake(SSLSocketImpl.java:1387)
at sun.net.www.protocol.https.HttpsClient.afterConnect(HttpsClient.java:559)
at sun.net.www.protocol.https.AbstractDelegateHttpsURLConnection.connect(AbstractDelegateHttpsURLConnection.java:185)
at sun.net.www.protocol.http.HttpURLConnection.getInputStream0(HttpURLConnection.java:1546)
at sun.net.www.protocol.http.HttpURLConnection.getInputStream(HttpURLConnection.java:1474)
at sun.net.www.protocol.https.HttpsURLConnectionImpl.getInputStream(HttpsURLConnectionImpl.java:254)
at com.codebyamir.ssl.App.main(App.java:18)If we wanted to trust the self-signed certificate from the previous example, we could add its root certificate to our truststore using the command covered previously in the keytool section.
After adding the certificate, running the code again successfully displays the page contents:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="/icons/favicon-red.ico"/>
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" href="/icons/icon-red.png"/>
<title>self-signed.badssl.com</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/style.css">
<style>body { background: red; }</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="content">
<h1 style="font-size: 12vw;">
self-signed.<br>badssl.com
</h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>Common SSL Validation Exceptions
Expired Certificate
When connecting to a site with an expired SSL certificate, we‘ll see the following exception:
java.security.cert.CertPathValidatorException: timestamp check failed
Wrong Common Name (CN)
When connecting to a site with a certificate name different than the hostname, we‘ll see the following exception:
java.security.cert.CertificateException: No subject alternative DNS name matching wrong.host.badssl.com found.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Does the JRE cacerts truststore get updated?
Yes, new releases of Oracle JDK/JRE will add new certificates to the truststore as needed.
How can I tell Java to use a custom truststore?
Add the following JVM property when starting the application:
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/app/security/truststore.jksIf the truststore password is different than "changeit", then also specify the password:
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=myTrustStorePasswordHow can I verify that a site is sending an intermediate certificate?
We can use the openssl utility on Linux to verify this:
openssl s_client -showcerts -connect google.com:443Java Developer's Guide to SSL Certificates
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/tang88seng/p/12090817.html
