


界面退出后进程程序还在运行,不会被杀死,如音乐播发器、后台下载等



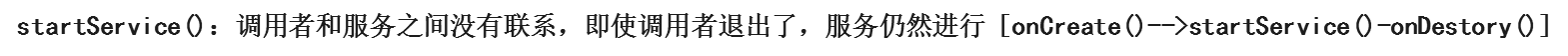

注:本文只讨论Started方式











main.xml代码分析
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnStartService"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Start Service"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnStopService"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Stop Service"
/>
</LinearLayout>
创建一个class类ExampleService.java
package com.szy.service;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class ExampleService extends Service
{
private static final String TAG="ExampleService";
@Override
public void onCreate()
{
Log.i(TAG, "ExampleService-->onCreate");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId)
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy()
{
Log.i(TAG, "ExampleService-->onDestroy");
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId)
{
Log.i(TAG, "ExampleService-->onStartCommand");
return START_NOT_STICKY;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent)
{
return null;
}
}
主对象类MainActivity.java
package com.szy.service;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
private Button btnStartService;
private Button btnStopService;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
btnStartService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnStartService);
btnStopService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnStopService);
btnStartService.setOnClickListener(listener);
btnStopService.setOnClickListener(listener);
}
private OnClickListener listener=new OnClickListener()
{
public void onClick(View v)
{
Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this, ExampleService.class);
switch (v.getId())
{
case R.id.btnStartService:
startService(intent);
break;
case R.id.btnStopService:
stopService(intent);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
};
}
在AndroidManifest.xml定义一下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.szy.service"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" />
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".ExampleService" />
</application>
</manifest>
时间: 2024-10-14 08:17:03
